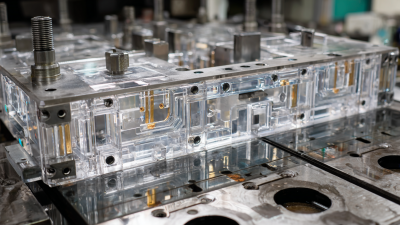
The automotive industry relies heavily on precision manufacturing. Among the essential components are turn signals. These small yet crucial devices help ensure safety on the road. To create them, manufacturers use an Automotive Turn Signal Mold. This mold shapes the plastic components precisely.
Creating an Automotive Turn Signal Mold requires careful planning. The process starts with designing the mold, which involves advanced technology. Each mold must fit perfectly. A slight error can lead to product failure. The design stage is where creativity meets technical skill.
Once designed, the mold is produced from durable materials. Common choices include steel or aluminum. These materials can withstand high pressures during production. The mold is then tested rigorously. Any flaws must be corrected before mass production begins. This stage shows how detail-oriented the industry is. There is always room for improvement, even in processes that seem straightforward.
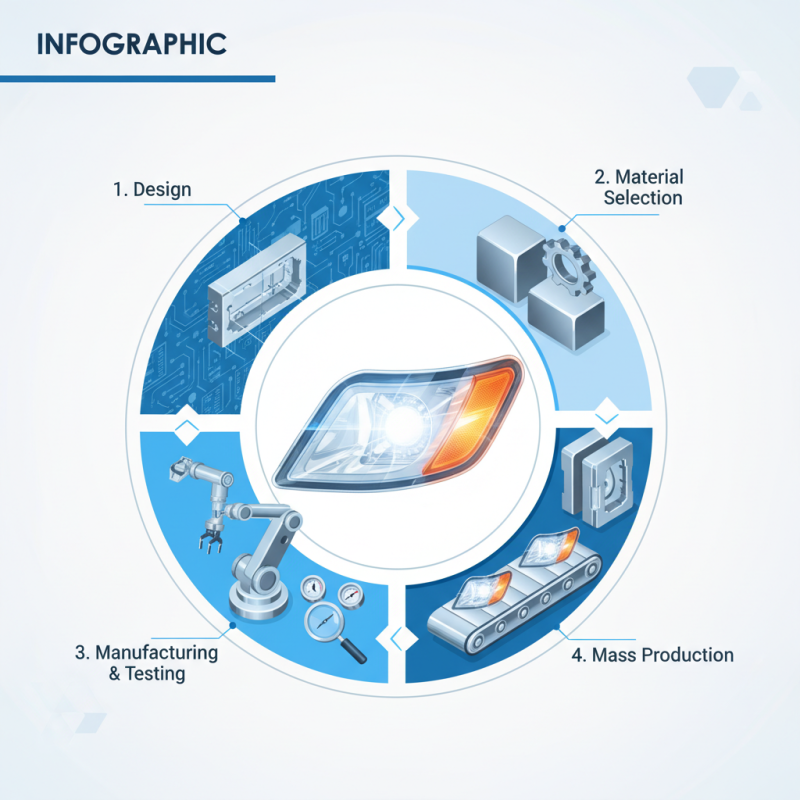
Automotive turn signal molds play a crucial role in vehicle safety and functionality. These molds are specialized tools used to shape the plastic housing of turn signals. Typically, they are crafted from high-strength materials like aluminum or steel, ensuring durability. The process begins with design specifications based on the vehicle model. Designers create a 3D model of the turn signal, which serves as the blueprint for the mold.
Once the design is complete, the mold-making process starts. It involves precision machining, where the material is cut and shaped into the desired form. This requires skilled workers and advanced technology. After machining, the mold undergoes polishing to ensure a smooth finish. Surface imperfections need addressing; even minor flaws can affect the final product's quality.
Tip: Regular quality checks during production can help identify issues early.
Next, the mold is ready for the injection molding process. Plastic pellets are heated and injected into the mold, taking its shape. Once cooled, the mold opens to reveal the turn signal component. It’s a delicate balance of speed and precision.
Tip: Always consider the prototype phase. It reveals design flaws that may need adjustments.
Overall, automotive turn signal molds are essential in manufacturing reliable signals that enhance road safety. Small details matter in this intricate process, and continuous improvement is key.
Automotive turn signal molds play a crucial role in vehicle safety. These molds are primarily made from materials such as thermoplastics, silicone, and aluminum. Each material has unique benefits that enhance the mold’s performance. Thermoplastics, for instance, are popular due to their excellent durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions.
Silicone molds are becoming increasingly important in the industry. They provide flexibility and can handle intricate design features. Studies show that about 35% of automotive manufacturers have begun using silicone due to its lower production costs and reduced waste generation. Furthermore, aluminum molds are favored for their ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. They ensure precise formation of the turn signal components.
Despite advancements, several challenges remain. For instance, achieving a balance between production efficiency and mold longevity is often difficult. Manufacturers frequently face issues with wear and tear, impacting quality. Additionally, environmental concerns are rising. Many companies must now consider how to reduce their ecological footprint during the manufacturing process. These factors are critical as the industry continues to evolve.
| Material | Description | Usage in Turn Signal Molds |
|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate (PC) | High-impact resistance and optical clarity. | Commonly used for transparent signal lenses. |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Good toughness and impact resistance. | Used for the housing of the turn signals. |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Lightweight and chemical resistant. | Utilized in internal components and connectors. |
| Silicone Rubber | Flexible, weather resistant, and durable. | Used for seals and gaskets. |
| Metal Alloys | High strength and durability. | Components like bulb sockets or clips. |
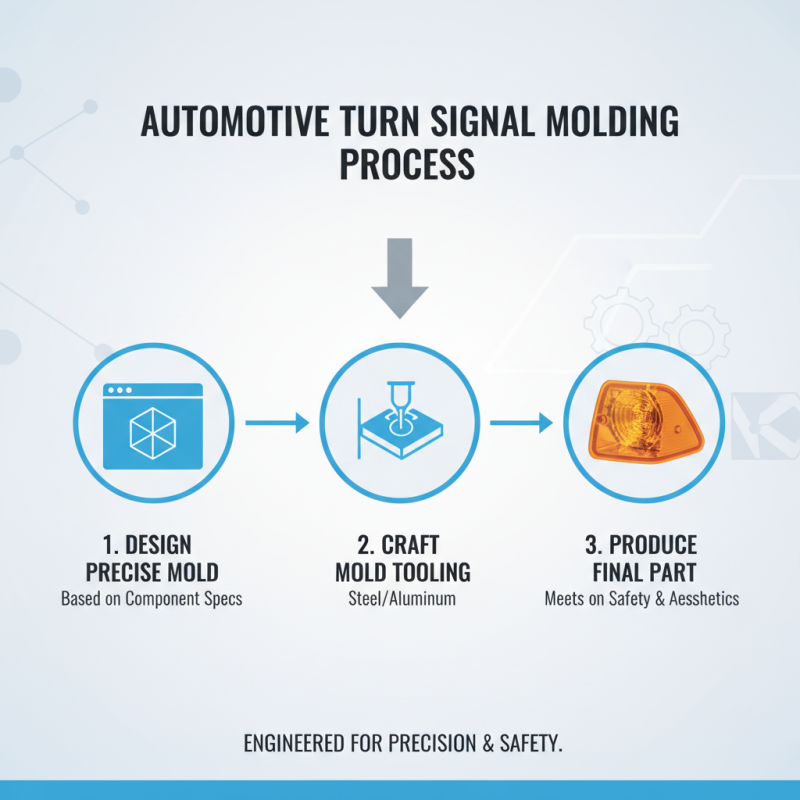
The molding process for automotive turn signals is intricate. It starts with designing a precise mold based on the component's specifications. The mold, often made of steel or aluminum, is essential for producing the desired shape. Engineers carefully plan the mold to ensure it meets safety and aesthetic standards.
Next, the selected plastic material is heated until it's malleable. The liquid plastic is injected into the mold under high pressure. This step requires precision to avoid defects. Once cooled, the mold releases the turn signal, forming a solid, durable component. However, imperfections can still occur. Tiny air bubbles or uneven surfaces might affect quality.
Tips: Always test prototypes thoroughly. This helps identify any flaws early in production. Maintaining a clean workspace also reduces contamination risks. Lastly, don’t rush the cooling process. Patience during this stage often leads to a better final product.
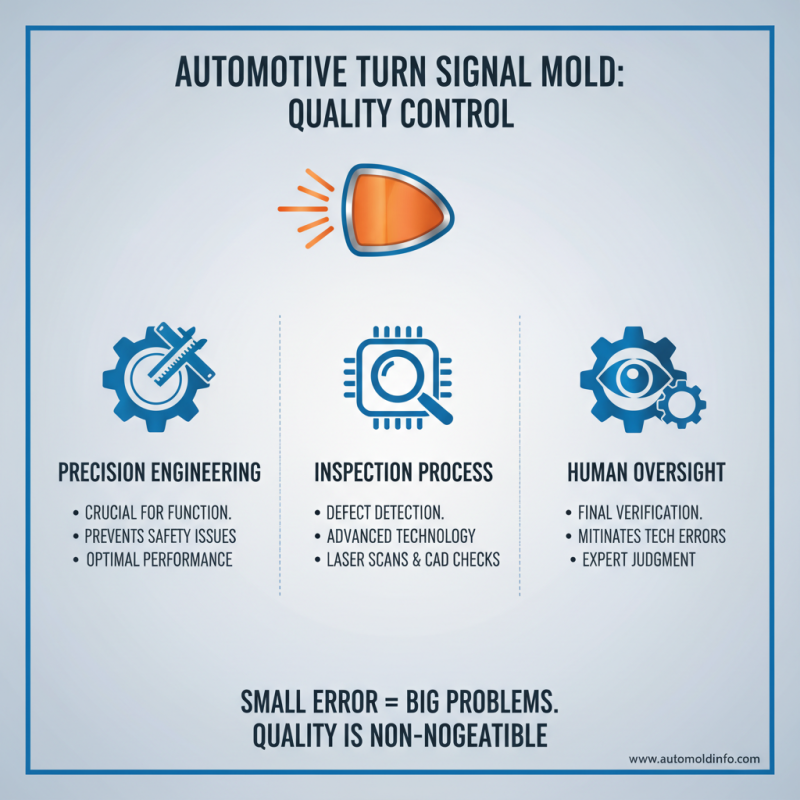
Quality control is crucial in the production of automotive turn signal molds. Each mold needs precision to ensure the signal lights work correctly. A small error can lead to significant issues in safety and performance. During the production process, careful inspections check for defects. These inspections often use advanced technology. However, human oversight is still necessary. Mistakes can happen, even with high-tech methods.
Tips: Always review production records. They help identify patterns in defects. Regular audits can reveal hidden issues.
Throughout the manufacturing process, communication among team members is vital. Every stage affects the final product. If one team misses a detail, it impacts the next. Managers should encourage feedback. It helps to detect and resolve potential problems early on.
Tips: Create an open dialogue. Encourage team members to share concerns. This can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
Investing in quality control measures pays off. Reliable turn signal molds ensure safety and performance in vehicles. Regular training keeps staff updated on best practices. Yet, it’s essential to remain adaptable. The industry constantly evolves, and so should production methods.
Automotive lighting components must meet strict industry standards. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) outlines these requirements for safety and performance.
Turn signals, a key element of vehicle lighting, must comply with these standards to ensure visibility and reliability.
Regulations typically focus on brightness, color, and response time. For example, turn signals should emit a specific color of amber light at a minimum intensity of 200 candela. This ensures that other drivers can easily notice the signal. However, not all manufacturers consistently meet these requirements. Reports indicate that up to 15% of vehicles may have inadequate signaling lights. Such discrepancies can lead to safety risks on the road.
Environmental considerations also play a role. As the industry shifts towards eco-friendly materials, some regulations are adapting. New standards encourage the use of recyclable components in lighting assemblies. This shift can complicate manufacturing. The balance between compliance and sustainability is an ongoing challenge for many producers. Efforts must be continuously evaluated to keep up with changing regulations while maintaining product quality.